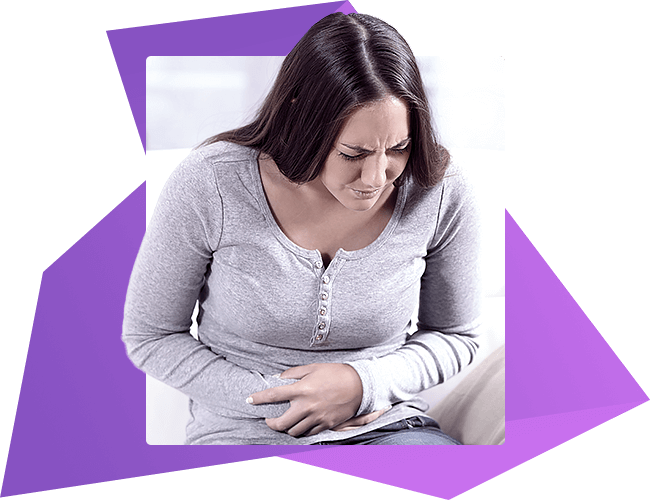
Stomach ulcer in children: what are the symptoms and how is it treated?
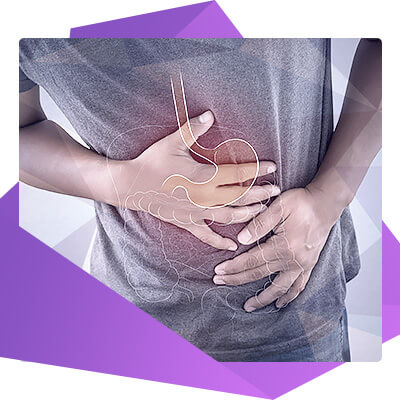
Stomach ulcer occurs in children from the age of 5 years. During the disease a lot of chronic mucosal deformities are formed. Such ulcers are hard to treat, sometimes surgical operations are required.
Stomach ulcer in children
Stomach ulcer in children is called internal erosion of an organ or 1st small intestine wall (12-front intestine). Such deformities are called peptic because they are associated with the effects of hydrochloric acid and a digestive enzyme (peptin) on cells. Therefore, stomach ulcer is called peptic.

Most often, an organ is affected on its back or front wall (in 85 percent) of the base of the 1st small intestine. Other patients have extra-vaginal ulcers. Affections of the 12-front intestine are seven times more frequent than in the stomach.
Code according to ICD-10
According to the international system of classification of all pathologies code for ICD-10 in gastric ulcer - K-25. If there was the same deformation of the 12-fringent bowel - K-26. Gastric ulcer is denoted by the K-28.
Classification of the disease
Peptic ulcer is divided into primary and secondary. Types of ulcers:
- caused by the microorganisms Helicobacter Pilori;
- peptic ulcers;
- idiopathic (Helicobacter-negative).
The disease may be acute or chronic with a tendency to relapse. In pediatrics, the most common is the classification of pathology by Masurin. Affection can be of three types:
- localized in the stomach;
- 12-tipersal colon;
- mixed form, combining the two previous species.
In the course of the disease is divided into lung, middle and severe. Classification by localization of ulcers (c):
- sub and cardiac divisions;
- body and stomach angle;
- astral;
- pyloric.
The disease has three phases - exacerbation, incomplete and complete remission. It is distinguished by a non- and complicated form. The disease may be with increased or decreased acidity. Endoscopically and clinically, peptic ulcer is classified into 4 stages:
- first - fresh ulcer;
- the second - the beginning of epithelization of the defect;
- third - healing;
- the fourth - remission.
In clinical form, the disease may have a typical and atypical form. Proceed with a pronounced pain syndrome. May not have it at all, but accompanied by other manifestations. The disease may also be asymptomatic.
In terms of size of neoplasm ulcers may be small (up to 0.5 cm), medium (no more than one cm), large (up to 3 cm) and giant (more than three cm). In terms of depth of penetration can distinguish between surface and deep lesions. Depending on the number - single and multiple.
Reasons for childhood ulcer
Stomach ulcer (photo in this article) appears under the influence of adverse endogenous or exogenous factors. The causes of the disease may be primary and secondary. In the first case, they are external:
- Inadequate or unreasonable intake of glucocorticoids, cytostatics and salicylates;
- dried food;
- bad habits (smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, use of drugs);
- swallowing large pieces of food that have not been chewed up;
- abuse of fatty and spicy foods (including marinades and sauces);
- inappropriate diet;
- Caffeine-containing foods and drinks;
- artificial feeding in the first year of a child's life;
- long breaks between meals;
- overeating.
Internal (endogenous) factors:
- inherited predisposition;
- excessive production of acid and pepsin (especially if they enter the stomach in large quantities);
- complications after a number of diseases (especially GIT pathologies);
- unfavorable course of pregnancy;
- gastrointestinal motor disorders;
- problem births;
- infection with Helicobacter Pilori microorganisms.
The causes of secondary peptic ulcers may be many factors:
- burns;
- liver cirrhosis;
- hypoglycemia;
- infections;
- craniocerebral injuries;
- autoimmune diseases;
- vascular insufficiency.
The secondary causes of ulcers include individual features of the body, stress, psychologically traumatic factors. Conflicting situations in kindergarten, school, and family have a negative impact on health.
Symptoms of ulcer disease
When a child has a stomach ulcer, symptoms depend on the localization of the lesion and the stage of disease development. The main symptom is pain. Characteristic feature is that it occurs after a meal. The early one makes itself known in half an hour or 60 minutes after meals, the late one - in 2-3 hours.
The pain (often severe) may occur at night. After eating food or liquid (apple, kefir), the negative sensations disappear. Pain can be cutting, seizure, stabbing. Give to the back, scapula or shoulder. Localization of pain depends on the location of the ulcer - more often appears on the right or in the epigastria.
During exacerbations, the disease is reduced if the child takes the position of "fetus", sits or lies down. With an ulcer in the front stomach, relief comes if the person lies on his back or bent back. Other symptoms of the disease:
- heartburn (usually appears before the pain). It may be at night, hungry, or periodic;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- burp;
- the tongue is covered with white patina;
- children may become constipated in case of exacerbations;
- there are signs of hypovitaminosis and moderate intoxication;###
- at palpation of the abdominal cavity painfulness appears;
- dizziness, weakness;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- abdominal cramps.
Hidden leaking ulcers - without pain or asymptomatic at all are dangerous risks of serious complications in the form of perforation or bleeding. In case of peptic ulceration of the site may additionally observed bloating of the abdomen, weight loss, digestive disorders.
Who treats peptic ulcer?
It makes no sense to go to him immediately, because the symptoms of the disease may be similar to other pathologies and to exclude them, the pediatrician prescribes a series of tests.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms of ulcer may be similar to other diseases (especially the gastrointestinal tract), an in-depth diagnosis is necessary. We study the state of the stomach and 12- finger gut.
First, a visual examination of the child, palpation of the abdominal cavity.
However, if the disease involves other organs, so a number of tests are taken and instrumental diagnosis is made.
Examination algorithm
After visual inspection and complaints of the child takes a number of tests. Then instrumental diagnosis is made:
- The main method is fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy. It allows you to take the material and for histological examination to exclude the presence of neoplasms.
- X-ray (including those with contrast). The child drinks barium suspension. The fluid is used to improve the quality of images of the intestine, esophagus, 12-frontal and stomach.
- The electrometric method helps to determine the level of acidity and assess its formation.
- When prescribing an ultrasound, parents are interested in seeing if an ultrasound of the stomach is possible. Yes, especially if the ulcer is large. Ultrasonic waves are not reflected in the affected area. On the pictures, you can see "holes" that indicate the possible presence of an ulcer. However, this should be complemented by other studies.
- Endoscopy to examine the digestive tract from the inside. A flexible tube equipped with light and a camera at the end is inserted into it.
In addition, a differential diagnosis is performed, during which duodenal probing is performed and the liver function is checked.
List of tests
To diagnose the disease it is necessary to take general tests of urine, feces and blood. Stomach contents are investigated. Feces are taken for latent blood. A breath test is made to check the presence of Helicobacter Pilori bacteria in the body. Histological tests are carried out (slices of biopsy are evaluated) and cystological tests (smears with mucous membranes are taken).
Treatment of the disease in children
The treatment of ulcer in children should be comprehensive. Taking medication must be combined with a diet. As auxiliary agents can be prescribed physical and phytotherapy. If necessary, a surgical operation is performed.
Medicament therapy
Medicament therapy is firstly aimed at eliminating symptoms of the disease, inflammatory processes. Can be used:
- antibiotics (depending on the reasons that caused the damage to the stomach);
- Proton pump inhibitors that block acid;
- H2-blockers that reduce the amount of pH that the stomach produces;
- drugs to protect the mucosa.
Then, ulcers are healed. Only then drugs are prescribed to restore normal gastrointestinal function.
Diet
The diet is made taking into account many factors - the form of disease, the level of acidity, the individual characteristics of the body, etc. Fractional nutrition (5-6 times) in small portions is necessary. The menu excludes spicy and fatty food and all products that enhance bile secretion - cakes, fats, yolks, sour cream.
Instead of whole milk, sour milk products are shown. All carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. Children should not be given chewing gum. If there are constipations, boiled beet is recommended. Dried fruit can be consumed only in steamed form. Food should be steamed, stewed or boiled.
Surgical intervention
Surgical operation is shown if the conservative treatment proved to be ineffective either in severe cases or when complications arise. Operations may be prescribed - vagotomy, resection, local excision, gastroenterostomy. Palliative suturing of the hole is performed (mainly in the presence of test ulcer).
Prevention of peptic ulcer
For prevention purposes, a child's diet should include all necessary vitamins. It is necessary to wash hands before eating, avoid starvation and overeating. A child should not be given fast food and should not be allowed to eat dry.
Meals are desirable at the same time. It is necessary to exclude all harmful products from the diet. It is necessary to take walks in the fresh air every day. Exclude stressful situations.
To undergo a scheduled medical examination.
Important information about children's ulcer disease is voiced in this video.
Advice to parents
These are the main measures to prevent the disease. If a child has complaints of pain, appetite disorders or other symptoms - you should immediately contact a pediatrician or gastroenterologist.
Consequences and prognosis
Without proper treatment (or its absence) a child may bleed. If there is a perforation (holes in the walls of the organ), food enters the abdominal cavity, which is normally sterile. As a result, there is inflammation (peritonitis), which can lead to death.
Sometimes, swelling and scarring of the stomach tissue appears as complications. As a result, the lumen of the intestine is severely narrowed or closed at all. Penetration may occur when the ulcer penetrates into other internal organs. This is accompanied by an increase in pain.
Other consequences of the disease include stenosis (when scarring the ulcer), perivisseritis (it is a soldering process that occurs between the liver, stomach, gallbladder and pancreas).
In the presence of timely and correct treatment, strict compliance with medical recommendations, ulcer disease is successfully treated, especially in the first stages. In this case, the therapy lasts about two weeks. If there are complications, the treatment will last longer. In case of complete remission, the child is removed from the dispensary within five years.
The first symptoms of stomach ulcer in children and the method of its treatment
Stomach ulcer in children occurs against the background of gastroduodenitis or gastritis. Stomach ulcer is chronic and develops for a long time, so it is not detected in children of early age.
There are teenagers in the risk zone, and the disease may show almost no signs, characterized by long periods of remission. The exacerbations usually occur seasonally, in spring or autumn.
Reasons
Factors that provoke stomach ulcers in children can be roughly divided into three groups:
- Exogenous or external.
- Endogenous or internal.
- Secondary factors that have an indirect impact on the development of the disease.
Among internal factors, the most common are:
- Active activity of Helicobacter Pilori bacteria. It is this microorganism that is the main provocateur of ulcers.
- Problems associated with the lack of motor skills of gastrointestinal tract organs. For this reason, there are stagnation and problems in the process of digestion of food.
- Disposition to the disease development on genetic level.
- Complicated course of other pathological processes, in particular, gastroenteritis or gastritis, which have a chronic character.
The most common external causes of ulcer disease:
- Poor nutrition: lack of a meal regime, consumption of potentially harmful foods.
- Treatment with the use of certain drugs.
- Lack of first courses in the child's daily diet.
- Overeating or having long breaks between meals.
- Frequent use of spicy and fatty dishes.
- Bad chewing of food.
The disease may develop under the influence of secondary factors:
- Stresses. Strong and prolonged stress states can create a favorable ground for the development of ulcers.
- Emotionality. A child may develop an ulcer in case of increased nervous excitability.
- The presence of factors that adversely affect the child's immature psyche.
Symptoms
The main sign of a stomach ulcer in children is a painful feeling in the navel area. At the same time, unpleasant sensations have the property of irradiation in the lower back and lower back area. As a rule, such pains are of rhythmic, periodic nature and can both increase and decrease as the disease progresses.
In children, stomach ulcers exhibit the following symptoms:
- burp, which has an acidic flavor;
- development of vegetative dysfunction;
- stool problems, when diarrhea alternates with constipation;
- severe heartburn.
This is the main symptomatology, which can be supplemented by other signs.
Important: If a child has at least two of the above attributes, you should immediately take him/her to a specialist. Symptomatic manifestation of the ulcer is often accompanied by colds.
As a rule, stomach pains in children increase in the morning, immediately after waking up. In half an hour after a meal, the pain syndrome may peak. It is also possible to show night pains, which can be reduced by drinking a glass of water or milk.
Abdominal pain may be different in nature, which depends on the localization of inflammation. During periods of exacerbation, the child subconsciously tries to take the position of the embryo by pulling his legs up to the stomach.
In this way he manages to reduce discomfort. If ulceration is formed on the front surface of the stomach, the patient should take the position lying on his back to reduce pain.
Complications
If a child's stomach ulcer is not treated in time, it can cause serious complications:
- Bleeding. This is one of the most common and dangerous consequences of peptic ulcer. With the development of internal bleeding there is a sharp deterioration of the patient's health, blood pressure drops, feces become black. Possible vomiting "coffee grounds", which directly indicates the development of bleeding.
- Penetration. The ulcer germinates through the stomach wall and extends to other organs located near the stomach. This is a very rare complication, which develops due to the wrong choice of therapy or prolonged neglect of symptoms of the disease.
- Renewal of the stomach. As a result of an ulcer, a through hole appears in the stomach wall, through which food may enter the peritoneum. In this case, the patient has a very strong painfulness. Such a state requires urgent hospitalization of the patient. As a rule, such a defect appears in the last stage of ulcer disease.
- Perforation. It is characterized by the development of severe pain that can cause the patient a state of shock.
Important: If the patient develops perforation against the background of ulcer, then in the process of palpation of the peritoneum, the specialist may note the disappearance of hepatic stupidity. This occurs due to the intake of air into the abdominal cavity.
Treatment
Treatment of stomach ulcer depends on a number of factors and is prescribed individually. During the development of the therapy course, the doctor takes into account the patient's body characteristics, age, the degree of progression of the pathology.
Medicines
The treatment of children with stomach ulcers is based on taking medications that are prescribed based on thorough diagnosis. These or other medicines are used in complex therapy depending on the degree of disease development. The most frequently used drugs are those of the following groups:
- Antibiotics. These drugs contribute to the destruction of the pathogens Helicobacter Pilori.
- Proton pump inhibitors. They are used to block the production of gastric acid.
- H2-blockers. Suppress the production of hydrochloric acid, destroying the mucosa of the gastrointestinal organs.
- Medicines that envelop the mucosa, which provide the necessary protection and prevent its further destruction.
Important: Most often children are prescribed vitamin complexes that help to improve their body's defenses.
Prophylaxis
To avoid the formation of ulcers, it is necessary to follow such recommendations:
- The elimination of stress.
- Proper nutrition.
- Adequate physical activity.
- Strengthening the immune system.
An ulcer is a serious disease that needs timely treatment. If a child has the first signs of illness, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Peptic ulcer in children - causes, symptoms, diet, treatment
Every disease that appears in a child is a matter of concern to parents. Peptic ulcer occupies a special place, because the immunity in children is not strong enough, and the appearance of ulcers may negatively affect the formation of other organs and systems of the body.
It is very important not to miss the first symptoms of the disease, to identify the causes of its occurrence and begin appropriate treatment.

The appearance of ulcer in a child is not a sentence for the rest of his life. The child's body reacts quickly to timely measures, and the probability of a complete healing of the ulcer is quite high.
However, it should be remembered that it is simply impossible to achieve a positive result without the participation of a gastroenterologist.
What is peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer is a violation of the integrity of the internal walls of the stomach or duodenum in the form of ulcers of different sizes. They are the result of exposure to the walls of the stomach acids, digestive enzymes, bacteria and many other factors.
The localization of these ulcers may be in different parts of the digestive tract. This disease is characterized by a long and persistent course, which is especially difficult for the child's body.
The appearance of ulcers on the shell of the stomach or duodenum in children (even very small ones) is no longer a rare phenomenon. Therefore, parents should arm themselves with information related to this pathology.
Classification
Treatment of any disease in a child requires a thorough examination. This is especially true for an illness such as an ulcer; its neglected form in children may become a serious problem in their future life. There is a medical classification of ulcer disease by various parameters.
By the place of localization:
- stomach;
- duodenum;
- double localization (in both organs).
According to the phase of the disease:
- exacerbation phase;
- phase of incomplete clinical remission;
- the phase of clinical remission.
In the form of the course of the disease:
- uncomplicated;
- with complications.
When choosing a treatment method, it is necessary to study and take into account each of these factors. The final result of the fight against the disease largely depends on it.
Causes of peptic ulcer in children
Identification of the causes of any disease is crucial in determining the method of its treatment. Stomach ulcers are no exception; their causes in children are similar to those in adults.
In the recent past, the main factors for the development of chronic stomach ulcer were considered the living conditions and diet (nervous overvoltage and dried-up meals). However, further medical studies have shown that there are many other reasons for the development of inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract. They are:
- Pylori Helicobacter bacteria. It is a unique pathogen that lives and multiplies in the gastrointestinal organs. The formation of most ulcers is associated with the effect on the stomach walls of this very bacteria.
- Chronic gastritis. Its appearance in a child should not be left without attention and treatment. In the future, it can provoke a weakening of the protective functions of the stomach and, as a result, the appearance of ulcers.
- Violation of the process of gastric secretion. Under certain circumstances, the failure of mechanisms involved in the process of gastric secretion occurs in the child's body. In this case, the increased secretion of acid that irritates the stomach walls begins. The probability of an ulcer in this case is very high.
- Occasional meals and long breaks between meals. Lack of diet impairs the ability of the stomach to protect itself from the aggressive effects of digestive enzymes.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Against the background of their uncontrolled use, a child often has this or that pathology in the gastrointestinal tract. Continued unjustified use of such drugs (Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Naproxen) may lead to ulcer formation.
- Chronic diseases. Diabetes mellitus, gallbladder disease may cause an increase or decrease in stomach motor skills. Such dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract contribute to the appearance of ulcer.
There are other factors that cause the weakening of the mucous layer of the stomach. They may include smoking, alcohol consumption, caffeine-containing drinks, prolonged physical activity, and injuries. In order to maintain the child's health, parents must exclude their appearance in the life of the child.
Treatment of peptic ulcer in the child
Many factors require the treatment of ulcer disease; when such disease is detected in children, these conditions fall on the parents' shoulders. They should remember that ignoring children's complaints and symptoms can provoke an aggravation of the disease. Unchecked medication can also make the situation worse.
If a child has an ulcer, only a child's gastroenterologist can choose and change the treatment method. Patient and careful adherence to all medical recommendations gives a chance for a full cure. Depending on the severity and type of illness, it can be cured using different methods of treatment.
Power Mode
Adjusting the power supply mode in certain cases can have a positive result. It is mainly applicable in the early stages of the disease. In this case, it can be used as an independent method, as well as part of a comprehensive treatment. Diet for ulcers should take into account all the nuances of the disease and features of the child's body.
Parents should follow a frequent (up to 6 times a day) diet, but in small portions. In this case, the products causing bile secretion are excluded - all fat, spicy, sour, salty. Preference should be given to cooked, stewed, steamy food. It is desirable for the child to eat food in a wiped form, especially in the period of exacerbation.
It is also important to observe the temperature regime of children's dishes. The food should be neither hot nor cold - to prevent any injury to inflamed mucous membrane tissues.
The exact list of permitted products for each specific diet is given by your doctor. The child's age and individual parameters are reflected in the recommended diet.
Medicines
In a more complex stage of the disease is prescribed medication therapy. Its primary goal is to stop the progression of the disease and all associated processes of inflammation. The reasons causing the disease are established; the following types of drugs are used for this purpose:
- antibacterial;
- acid blockers;
- H2-blockers;
- enveloping (to protect the mucous membrane);
- preparations that promote mucous membrane regeneration and healing of ulcers.
As an addition, sedatives (motherwort, valerian) can be prescribed.
In the final stage of the drug therapy process, drugs are used that can restore the functions of the gastrointestinal organs. The complex therapy may also include in the future:
- physiotherapy;
- medicines of plant origin for healing and scarring of ulcers;
- therapeutic mineral waters.
All these activities are prescribed based on the degree of disease, age and features of the child's body.
Peptic ulcer in children: symptoms, 6 causes, methods of treatment
Peptic ulcer is an erosion of the inner surface of the stomach or duodenum (first part of the small intestine). These erosions are called "peptic" ulcers because they are related to the activity of acid and pepsin (digestive enzyme) on cells.
Peptic ulcer in the stomach is called gastric ulcer. If it is in the duodenum, it is duodenal ulcer (JADD).
Symptoms of a stomach ulcer and duodenal ulcer
- The main sign of peptic ulcer is abdominal pain.
The pain is described as chewing or burning, usually localized in the epigastric (upper) abdominal region or just below the ribs on the right or left side.
The specificity of the pain depends on the location of the ulcer. In children with gastric ulcer, the pain often increases with food, and sometimes a child with a stomach ulcer can even subconsciously reduce food intake and even lose weight.
On the contrary, duodenal ulcer in children usually causes pain between meals when the stomach is empty. And the pain is often relieved when eating. Such children rarely lose weight and may even gain it.
- If a child's stomach ulcer becomes large enough, it destroys the blood vessel and bleeds. Doctors call it "upper gastric bleeding," as the place of bleeding is in the upper parts of the digestive system.
Symptoms in this case can be very dramatic (eg, vomiting bright red blood), and they can not be ignored.
If the bleeding is very small, the symptoms may be less pronounced:
- weakness from anemia, dizziness;
- rapid heartbeat;
- abdominal spasms caused by the movement of blood that irritates the intestines;
- tarmac stool formed by the digestion of blood in the intestine.
Peptic ulcer located at the junction of the stomach and duodenum causes swelling in the lining of the stomach, which in some cases provokes the development of partial obstruction.
If this is the case, the symptoms may include bloating, severe digestive disorder, nausea, vomiting and loss of body weight. Children with peptic ulcer also have a relatively high chance of developing gastroesophageal reflux disease and related symptoms, especially heartburn.
The symptoms of gastric and duodenal ulcer in children may resemble other pathological conditions in the digestive system or health problems. Therefore, in case of such complaints, an in-depth examination is necessary.
In the past, it was believed that stress and malnutrition cause this disease. Later, researchers said that gastric acids contribute to the formation of most ulcers. Today, however, studies show that most ulcers develop as a result of infection with a bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
1. Helicobacter pylori
Studies have shown that most ulcers are caused by Helicobacter pylori. Although other factors listed below may also cause it, H. pylori is now considered the main cause of most of them. This bacteria lives in the stomach and, along with the acid secret, damages the stomach and duodenal tissues, causing inflammation and ulcers.
2. Acid and pepsin
It is believed that these powerful digestive juices contribute to the formation of ulcers. In ideal situations, the stomach can protect itself from these fluids in several ways:
- The stomach produces mucus that covers the walls. It protects the tissues from the aggressive effects of digestive enzymes;
- The stomach can produce a chemical called bicarbonate, which neutralizes excess acid and decomposes it into less harmful substances;
- circulation in the lining of the stomach, as well as renewal and active cell regeneration help protect the stomach.
3. non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The most famous NPVPs are Aspirin, Ibuprofen and naproxene sodium. They are present in many over-the-counter drugs used to reduce fever, relieve headaches and other pains.
HPVPs can affect stomach protection mechanisms in several different ways:
- They can make the stomach vulnerable to harmful effects of acid and pepsin, preventing the stomach from producing mucus and bicarbonate;
- they can affect cellular repair and blood flow in the stomach walls.
4. Smoking teenagers
Studies show that smoking cigarettes can increase a teenager's chances of developing an ulcer. Smoking inhibits the healing of existing ulcers and encourages relapse.
5. Caffeine
Drinks and caffeine-containing foods stimulate acid production, which can aggravate existing ulcers.
But the stimulation of gastric acid cannot be ascribed to caffeine alone.
6. Stress
Emotional stress is no longer considered responsible for ulcer disease, but children experiencing it often report increased pain from existing ulcers.
However, physical stress can also increase the risk of ulcers, especially in the stomach. For example, children with injuries (severe burns) and children who have undergone serious surgery often need careful treatment to prevent ulcers and complications.
Without proper treatment, a child with ulcer may have serious complications.
The most common problems:
- hemorrhage. Since the inner surface of the stomach or duodenum wall is damaged, blood vessels may also be partially destroyed. This causes bleeding;
- perforation (loss of integrity). Sometimes there are deep defects in the walls of the stomach or duodenum, and bacteria and partially digested food can seep through the resulting holes in the sterile abdomen and cause peritonitis (inflammation of the abdomen) and inflammation of the abdominal cavity itself;
- narrowing and obstruction. Ulcers in children located in the weekend areas of the stomach can cause swelling of the tissues and the formation of scars that narrow or close the lumen of the intestine.
Treatment of children's ulcers
Treatment will depend on the symptoms of the child, age and general health.
Lifestyle change
In the past, doctors recommended not to give a child with ulcer disease spicy, fatty or sour foods. However, a mild diet is now known to be ineffective in treating or preventing ulcers.
No specific diet can help most children with peptic ulcer. If some foods seem to make things worse, discuss the problem with your doctor.
Some teenagers smoke cigarettes. Parents do not always know what their children smoke. Smoking slows down the closure of the ulcer and provokes the disease.
Doctors can treat gastric and duodenal ulcers with several types of medicines:
- antibiotics. They are used to kill bacteria;
- H2-blockers. They reduce the amount of acid that the stomach produces by blocking histamine, a powerful stimulant of acid secretion;
- proton pump inhibitors. They more fully block the production of gastric acid by stopping the acid pump of the stomach, the final stage of acid secretion;
- mucous membrane protection products. These drugs protect the stomach mucosa from acid damage. They do not affect the production of gastric juices.
In the treatment of H. pylori, these drugs or procedures are often used in combination.
Taking care of children
If the child is diagnosed with ulcer disease caused by H.pylori, make sure that the child takes all antibiotics as directed by the doctor. Even if the symptoms go away, the infection may not disappear until the treatment is over.
- If the ulcer in children is associated with medication, your doctor will advise you to avoid HPVP, including any medication containing Ibuprofen or Aspirin;
- in addition, be sure to give your child a prescribed acidity reduction medication;
- most doctors do not recommend diet restrictions for a child with ulcer. A good diet with a variety of foods is important for the healthy growth and development of your baby;
- also make sure that your child avoids coffee, tea, carbonated beverages and caffeine-containing foods that stimulate acid production in the stomach and exacerbate the ulcer.
Preventing the infection with Helicobacter will reduce the risk of peptic ulcer in the child. It is not yet clear how this infection is spread. But the following measures will help to reduce the risk of peptic ulcer in the child:
- wash your hands often;
- not to contact with people who have manifestations of peptic ulcer;
- not to eat or drink dirty food and water.
Children's ulcer may be an unpleasant experience for parents and children, but with timely and proper treatment, almost all ulcers are cured.
Peptic ulcer in children: symptoms, causes and treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers
If previously an ulcer was found in schoolchildren, it is now diagnosed in children under 5-6 years of age.
Without appropriate treatment of gastritis and gastroduodenitis, the ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the stomach, and eventually on the duodenum. Various symptoms testify to the presence of ulcers.
One of the main signs is a child's complaint of abdominal pain after a meal or at night.
Symptoms and causes of peptic ulcer development in childhood
The symptomatology of the disease depends on the degree of inflammation and the location of the ulcer on the mucosa. The signs of the disease are:
- white plaque on the tongue and an unpleasant smell from the mouth;
- heartburn;
- burp;
- nausea and vomiting;
- constipation in the acute phase.
In rare cases, the ulcer occurs against the background of problems with the cardiovascular, urinary and respiratory systems. Common causes of stomach and duodenal ulcer are:
- gastroenterological diseases;
- presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the body;
- errors in child nutrition;
- psycho-emotional trauma or stress in children;
- treatment with certain types of medicines (glucocorticosteroids, aspirin);
- genetic predisposition.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made on the basis of an examination by a doctor, taking into account the complaints of the young patient. Laboratory tests are carried out to confirm the disease:
- blood and feces analysis;
- examination for Helicobacter Pilori with a breath test;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- differential diagnosis, which consists of duodenal probe and study of gastric juice in remission;
- X-ray contrast examination;
- determination of the level of acidity in the stomach through the electrometric method;
- if there is a risk of blood vessels narrowing or ulcers appearing not only in the stomach but also in the 12 colon, the child will be examined by CT;
- biopsy testing of tissue from the stomach.
Ulcer treatment for children
Treatment of the disease at the initial stage involves a conservative method. In case of exacerbation of the disease the child is treated in hospital for 7-14 days. In complex cases, surgical intervention is performed. The doctor chooses medicines for the treatment of ulcer disease taking into account its severity, causes, as well as the age of the child and associated pathologies:
- The most common culprit of ulcer development is Helicobacter Pilori. In such cases, 3 drugs are prescribed - antibiotic (Clarithromycin, Amoxiclav), nitrupharone (Nifuratel, Furazolidon), a drug to reduce the production of gastric acid (Omez, Omeprazol).
- Antacids (Maalox, Almagel) are used to reduce the activity of the acid-enzymatic factor.
- Sedatives (valeriana).
- Medicines for the recovery of mucous stomach (Riboxin, Pentoxyl).
- When the contents of the duodenum are abandoned, enterosorbents are prescribed (Enetrossgel, Smekta).
- To reduce muscle tone - No-Spa, Papaverine.
- For severe nausea and vomiting - Motilium, Cerukal.
- Phyto preparations (sea buckthorn oil, propolis, Alanton, Plantaglucid) are used for healing.
Diet for peptic ulcer
Proper nutrition for your baby is a prerequisite for successful treatment of the disease. It is recommended to adhere to the following systems: the first week - Pevzner's diet, table number 16 - for the second and third weeks, table number 1 for 40 days and table number 5 for two years. Dietary rules:
- Exception of spicy, sweet, salty, fried, fatty dishes and carbonated drinks;
- food must be warm;
- preference should be given to liquid soups and mashed potatoes;
- you should not eat dry;
- it is recommended to eat fractional meals;
- daily salt consumption - not more than 8 grams;
- chew the food well.
Complications and forecasts
Complications happen in 7-10 percent of children. These are often neglected cases that were not treated in time. Complications of peptic ulcer include:
- internal bleeding (vomiting and feces with blood);
- stenosis - stomach dilation with signs of intoxication;
- penetration - the appearance of ulcers outside the stomach;
- perforation - the breakthrough of ulcers into the abdominal cavity;
- malignization - regeneration of a wound into a cancerous tumor.
By: Dr. Michael Dann